The link between physical and mental health: Mood, sleep and stress influence your sense of control
05/20/2019 / By Zoey Sky

Getting enough sleep at night ensures that you wake up well-rested the next day. In fact, an interesting study suggests that your mood, sleep quality, and stress levels can all affect your “control beliefs.”
The paper, titled “Predicting Control Beliefs in Older Adults: A Micro-longitudinal Study,” was published in the Journal of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences. The study was conducted by researchers from North Carolina (NC) State University.
In the study, psychology researchers discovered another reason why mood, sleep, and stress are vital to your overall health: these three factors “affect the extent to which older adults feel they have control over their lives.” The researchers believe that the findings can be used to develop useful techniques to improve a person’s sense of control, which is crucial for one’s physical, mental, and emotional health.
Shevaun Neupert, a professor of psychology at NC State and co-author of the study, explained that mood, sleep, and stress are important factors that help determine someone’s sense of control. Neupert added that these results are important because when older adults start to lose their sense of autonomy, it may cause changes in behavior that can negatively affect their well-being.
What are “control beliefs?”
In the study, researchers evaluated data on 205 participants aged 60 to 94. The study volunteers provided information on various psychological variables on eight days for three weeks.
The researchers wanted to confirm if there were variables that could affect two particular “control beliefs”:
- Perceived competence – This refers to your sense that you can do the things you wanted to do.
- Locus of control – This refers to the sense that you are in control of your own life.
Findings revealed that several variables significantly affected both beliefs. The first is sleep efficacy or the belief that you can get a good night’s sleep, which was linked to better control beliefs.
Shenghao Zhang, a doctorate student at NC State and first author of the paper, shared that being in a good mood made people feel better about their competence and control, but being in a bad mood made them feel worse.
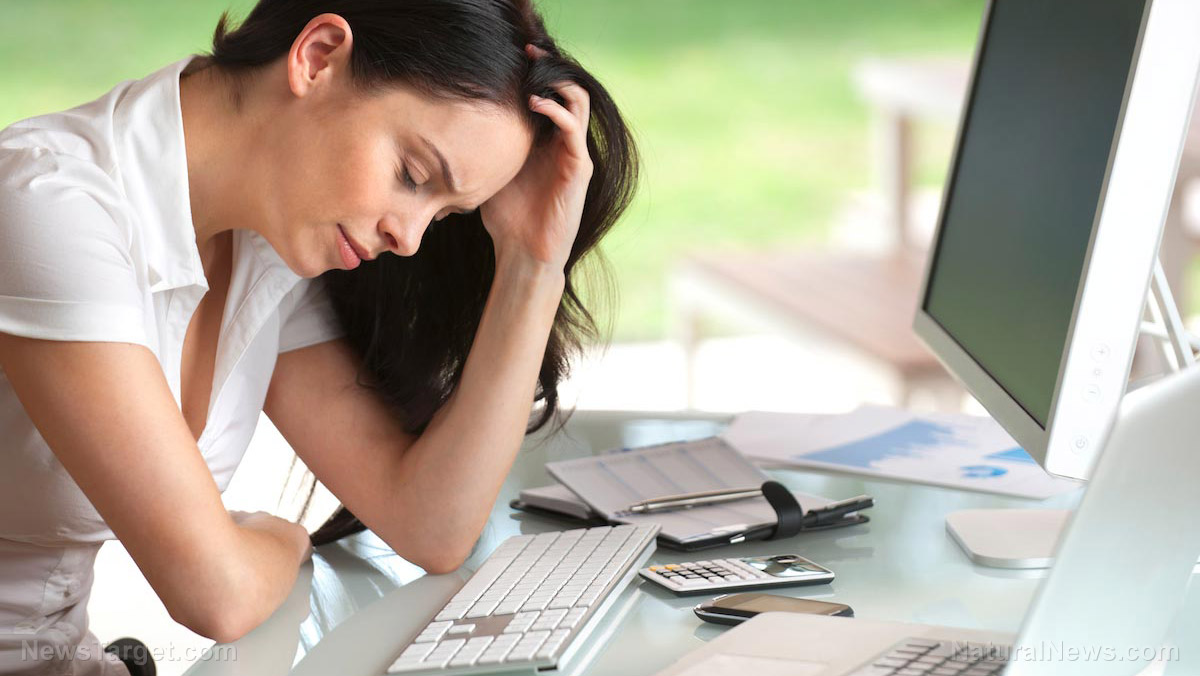
Finally, the results showed that stressful events on one day negatively affected someone’s subsequent control beliefs. Zhang added that according to the results, the negative effect of stressful events could last for longer than one day. (Related: Brain fog is caused by lifestyle: Doctor reveals how diet, stress levels and sleep affect hormones, performance and immunity.)
Neupert advised that there are several ways to improve your mood and sleeping habits. He noted that the study highlights specific reasons why both sleep and mood are crucial for your health.
According to Neupert, if you start thinking that you have little or no control over your life, there’s a chance that you might stop practicing self-care. However, self-care is crucial since mood, sleep, and stress are three factors that can be improved through self-care practices like de-stressing and having healthy sleep habits.
Neupert concluded that older adults could retain their sense of control and quality of life by prioritizing these factors and improving their overall well-being.
Tips to improve your sleep habits
You can maintain your control beliefs by practicing good sleeping habits since sleep significantly affects your mood and stress levels. Follow the tips below if you want to get a good night’s sleep.
- Have a relaxing bedtime ritual. Before you go to bed, a relaxing activity like reading or listening to calming music can help you fall asleep better.
- Follow a sleep schedule with the same bedtime and wake up time. It helps to do this even on the weekends so you can regulate your body clock.
- Evaluate your bedroom. Make sure your room is dark, cool (between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit, and quiet before you turn in for the night.
- Make sure your bedroom is free from distractions. This means you shouldn’t have a TV and devices like your phone in your room. Keep the TV in your living room and don’t use your phone before you go to bed. The screens of these devices emit a particular type of light that activates your brain, making it hard to fall asleep.
Sleep in a cool, dark room and avoid distractions, so you can easily fall asleep during bedtime. Having healthy sleep habits can help ensure that you wake up in a good mood every morning.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: brain function, cognitive health, control, control beliefs, destressing tips, emotional health, mental health, mind body science, mind-body medicine, mood, neurocognitive health, physical health, Psychology, research, self-care, sense of control, sleep, sleep efficacy, sleep habits, sleep quality, stress, stressors
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
BrainFunction.News is a fact-based public education website published by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.