Do you have enough tryptophan in your diet?
12/03/2019 / By Melissa Smith

Also known as L-tryptophan, tryptophan is an amino acid used in the biosynthesis of proteins. In infants, it is important for normal and healthy growth. In adults, it maintains nitrogen balance.
Tryptophan is also needed to make niacin, which is important for producing the neurotransmitter serotonin. Serotonin promotes healthier and better-quality sleep, relieves depression and anxiety, improves emotional well-being and manages pain tolerance.
Tryptophan also plays a role in cognitive function, being a precursor to serotonin. Low serotonin levels are associated with impaired memory. A study published in the journal Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care also found a link between tryptophan and cognitive function. Another study published in 2017 suggested that tryptophan could potentially be used for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. (Related: Tryptophan found to be necessary for better mental health.)
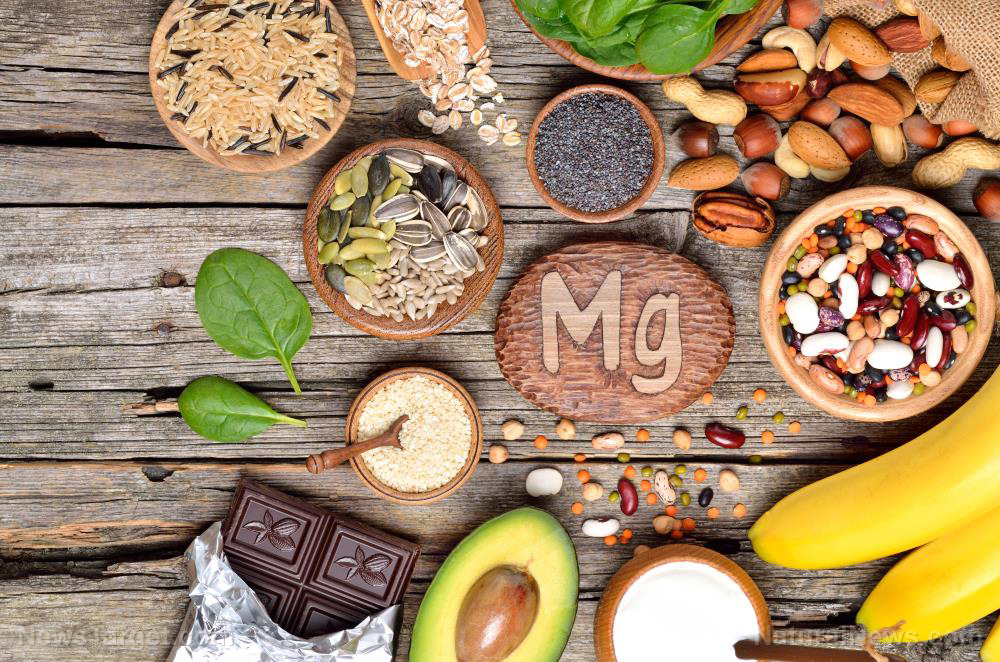
This essential amino acid is needed by the body and can be obtained from tryptophan-rich foods, such as:
- Bananas – Bananas contain tryptophan, among other nutrients. Eating bananas every day can improve your mood and regulate the release of serotonin.
- Eggs – Eggs, especially egg whites, are loaded in tryptophan and tyrosine. These two amino acids greatly contribute to the antioxidant properties of eggs.
- Poultry – Turkey and chicken are great sources of tryptophan. A portion of four ounces of chicken or turkey contains 350-390 mg of tryptophan.
- Red meat – Red meat like beef, lamb, and pork are rich in protein and provide a good amount of tryptophan. However, they also contain high amounts of saturated fats that can increase your cholesterol levels. Therefore, it is important to limit your intake of red meat to prevent diseases.
- Seafood – Seafood is also a great source of tryptophan. Shrimp contains the highest amounts of tryptophan, with 330 mg for a 4-ounce serving. Salmon, cod, tuna, sardines, crab, scallops, and other seafood also offer about 250-400 mg of tryptophan per serving.
- Dairy products – Organic dairy products like cheese, milk, and yogurt provide good amounts of tryptophan, but not as much as fish and eggs.
- Soy products – If you are a vegetarian or vegan, you can get tryptophan from soy products, such as tofu and soybeans.
- Nuts and seeds – Eating nuts like almonds, cashews and pistachios, as well as edible seeds like chia, pumpkin seeds, flaxseeds, sesame seeds and sunflower seeds can provide high amounts of tryptophan, which can increase your serotonin level.
- Legumes – Black beans, kidney beans, lentils, and peanuts are some of the legumes that contain high amounts of tryptophan. For better health, aim to eat at least ¼ cup of legumes in your everyday diet.
In addition to these foods rich in tryptophan, you can get tryptophan through supplements. Tryptophan supplements are available in 500 and 1,000 mg tablets and capsules. Taking tryptophan supplements 15 minutes before mealtimes or two hours after eating can help increase its absorption in the body.
However, it is best to consult your healthcare provider first before taking any tryptophan supplement to prevent side effects. In some cases, tryptophan supplements can cause belching, diarrhea, heartburn, stomach pain, loss of appetite, vomiting and nausea. It may also cause weight loss, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue and heart palpitations. Additionally, avoid taking tryptophan supplements with other medications.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: brain health, cognitive health, disease treatments, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, nutrients, prevention, supplements, tryptophan
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
BrainFunction.News is a fact-based public education website published by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.