Not getting enough magnesium? You might be at risk of heart disease, depression
11/27/2019 / By Melissa Smith

Being deficient in nutrients comes with serious health risks. Having low levels of magnesium, for instance, can increase your risk of cardiovascular diseases and depression.
In a study published in the journal Atherosclerosis, researchers found that people with low magnesium levels are at risk of developing peripheral artery disease (PAD). When the participants increased their magnesium intake, the risk of PAD consequently decreased.
PAD is a circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. This causes a notable pain in the leg when walking. This disease is also likely to be a sign of a more widespread buildup of fatty deposits in your arteries, which may also lead to reduced blood flow to your heart and brain.
Magnesium deficiency also increases the risk of other cardiovascular problems. Magnesium is an important mineral needed for healthy blood vessel function, blood pressure regulation, and normal heart contractions. Having low magnesium levels may increase your risk of conditions like endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmia.
Low magnesium levels linked to depression
Having low levels of magnesium does not only affect your cardiovascular health, but also your mental health. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Internal Medicine Journal found a link between magnesium deficiency and depression. This research looked at six observational studies with a total of 19,137 participants. (Related: Why you need magnesium if you’re constantly stressed or anxious.)
One study, which was published in the journal PLOS One, suggested that supplementing with magnesium may help treat depression after researchers found that increasing magnesium intake led to an improvement in depression symptoms.
For this study, a team of researchers from the University of Vermont recruited 126 adults with mild or moderate depression. They asked half of the participants to take magnesium supplements for six weeks, followed by a six-week control period without magnesium. The other half were asked to take magnesium supplements after a six-week control period. The research team monitored the participants’ symptoms and side effects through phone calls every two weeks.
How to increase your magnesium levels
The recommended daily intake of magnesium is 400 milligrams (mg). However, nearly half of Americans aren’t reaching this guideline. The symptoms of magnesium deficiency are typically subtle unless your levels become severely low. It may cause fatigue, irregular heartbeat, mental problems, muscle cramps, and osteoporosis. You can take a simple blood test to check whether you’re deficient.
One way to increase your magnesium levels is to take supplements two times a day with meals. Make sure that you are taking high-quality oral magnesium supplements. The best kinds include magnesium chloride, magnesium citrate, and magnesium lactate, as they are better absorbed by the body than other options. Avoid taking magnesium oxide because it forms a caustic magnesium hydroxide in the body that can burn the intestinal walls. It is also poorly absorbed.
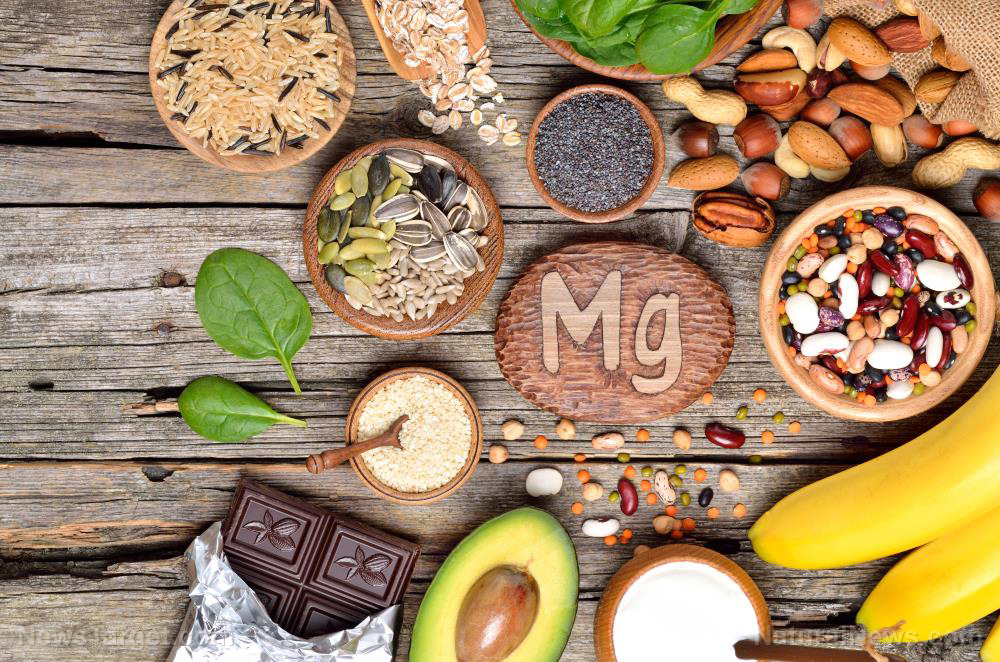
Aside from taking supplements, you can increase your magnesium levels through food. Healthy foods rich in magnesium include the following:
- Avocados
- Black beans
- Cooked spinach
- Dark chocolate
- Nuts, such as almonds, Brazil nuts and cashews
- Pumpkin seeds
- Salmon
- Tofu
You also need to avoid foods that cause magnesium levels to decline, such as:
- Alcohol
- Cheap common table salt (use good-quality Himalayan crystal salt or Celtic Sea salt instead)
- Gluten
- Non-organic produce (they contain harmful herbicides and pesticides that can deplete magnesium)
- Refined sugar, such as corn syrup and artificial sweeteners
- Other refined foods, such as unfermented soy products
- Regular and decaffeinated coffee or black tea
- Tap water (it is laced with poisonous sodium fluoride)
Furthermore, you also need other nutrients to utilize, absorb, and keep magnesium in your body. Make sure you get enough vitamins E, B6, and D3, thiamine, and selenium. Keep your brain and heart health healthy by reading more articles at MindBodyScience.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: brain health, CVD, depression, heart health, Magnesium, magnesium deficiency, mental health, mind body science, nutrients, research, supplements
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
BrainFunction.News is a fact-based public education website published by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.