Green tea food therapy: Calm anxiety with this zesty matcha-blackberry pudding
09/25/2020 / By Zoey Sky

Following a healthy diet keeps your body strong and healthy. But did you know that consuming antioxidant-rich superfoods like green tea can also help relieve anxiety and promote brain health?
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize free radicals that can damage your cells. Your body naturally produces these compounds, but you can also get them by eating nutritious fruits and vegetables. Antioxidants are crucial to your overall health because they boost your immunity, keep your skin looking young and promote cognitive and mental health.
In The Anti-Anxiety Cookbook, Ali Miller, a registered dietitian, explained that eating the right kinds of foods is essential to promoting your overall health.
Amino acids, GABA and neurotransmitters
Your central nervous system releases billions of neurotransmitters that act as biological signals in your brain. Neurotransmitters are important because they’re involved in various bodily functions, such as cognitive processing, perception and mood regulation.
Amino acids serve as the building blocks of neurotransmitters. These compounds combine in the presence of specific enzymes and cofactor to form neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are needed to manage inflammation and cognition, as well as to drive different autonomic nervous system functions.
The neurotransmitters of your central nervous system communicate directly with those produced in the gut via the enteric nervous system. The latter has more neurons than the central nervous system, which is made up of your brain and spinal cord. (Related: Regular tea consumption linked to healthy cognitive function: Study.)
There are two categories of neurotransmitters: Excitatory, which stimulate neurons, and inhibitory, which reduce neuron activity.
Your adrenal glands release catecholamines, which are stress-responding excitatory neurotransmitters that include dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine, when you switch to the “fight-or-flight” mode.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate anxiety and depression. When GABA attaches to a brain protein called GABA receptor, it produces a calming effect that can relieve feelings of anxiety, fear and stress.
Aside from balancing mood and inducing calm, GABA offers anti-inflammatory effects on your gut, which then minimizes the response of inflammatory chemicals and compounds. GABA also helps lower epinephrine, which can trigger irritability, panic or worry at high levels.
Diet and neurotransmitter levels
Following a balanced diet full of amino acids like glycine, tryptophan and tyrosine helps boost GABA production and has a calming effect. Foods rich in these amino acids include grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry and pork, along with bone broth and gelatin.
At the same time, you need to boost your protein intake for “foundational amino acid support.” Eating grass-fed, pasture-raised meats and wild-caught fish gives your body access to high-quality sources of important nutrients that don’t contain high amounts of pro-inflammatory compounds.
Follow the tips below to optimize your neurotransmitter levels:
- Consume enough protein. You need to eat at least half a gram of protein per pound of your body weight daily.
- Boost your gut health by consuming foods full of probiotics, like cultured vegetables and fermented foods.
- Take amino acid supplements like L-theanine, serine, tryptophan and tyrosine.
- Reduce screen time and wear blue blockers or special lenses that block blue light. Using electronics too much and being exposed to blue light for too long may burn out your dopamine.
- Get at least seven to nine hours of sleep every night.
- Practice mindful habits like deep breathing or yoga to manage your stress levels.
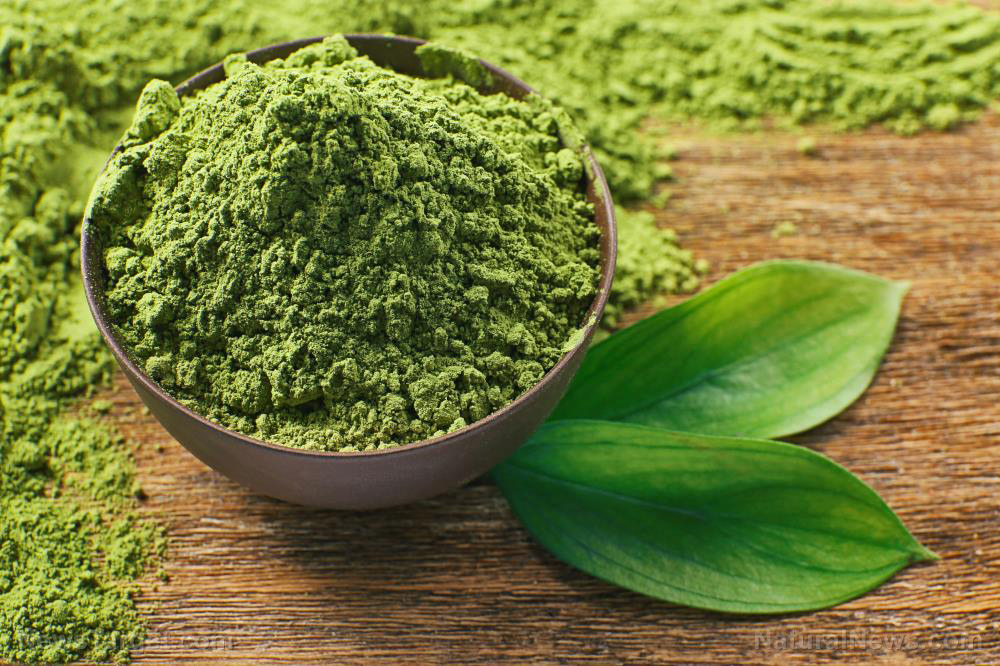
Matcha-blackberry pudding recipe
Alternatively, you can make an antioxidant-rich matcha-blackberry pudding that will help rebalance your neurotransmitters. This creamy, zesty pudding combines superfoods like green tea (also called matcha) powder with the bright, acidic notes of lime and blackberries.
Matcha contains L-theanine, an amino acid that makes you feel more alert and aids in alpha brainwave production. If you prefer a heavier snack, use additional toppings like chopped nuts, coconut shreds or hemp seeds when making your pudding.
Ingredients for 4 1/2 cup servings:
- 1 (13.5-ounce) can of full-fat coconut milk
- 1 cup of fresh blackberries
- 2 tablespoons of lime juice
- 1 tablespoon of lime zest
- 1 tablespoon of gelatin
- 1 tablespoon of honey
- 2 teaspoons of matcha tea powder
- 1/2 teaspoon of lemon extract or lemon juice
Preparation:
- Combine all the ingredients, except the blackberries, in a blender. Mix on high for one minute.
- Let the mixture rest for five minutes to bloom the gelatin, then blend it on high for another minute.
- Divide the pudding into four ramekins or Mason jars. Refrigerate the pudding for eight to 10 hours or overnight.
- Top each ramekin with 1/4 cup of blackberries before serving.
Follow a balanced diet and enjoy a serving of zesty matcha-blackberry pudding to minimize inflammation and relieve anxiety.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: anti-inflammatory, antioxidants, Anxiety, brain function, brain health, food cures, food is medicine, food therapy, functional food, Green tea, inflammation, natural medicine, Neurotransmitters, prevention, pudding, recipes, tea
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
BrainFunction.News is a fact-based public education website published by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Brain Function News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.